Dataset Collection and Aggregation
Learn how Envision performs data collection and data aggregation.
Supported Envision Versions: 1.0, 1.1, 1.2
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Data Collection Using a Broker
- Data Collection Using Individual Transactions or Raw Data
Introduction
In the previous topic we introduced the concept of a dataset, how metrics are defined, their aggregation, and collection intervals. In this topic we will describe how the data in a dataset is actually collected and how the aggregation is performed.
Note: Wherever the data is coming from, it must be of the correct data type defined in the dataset. Envision validates the data type, and data of an invalid data type is discarded. If the dataset definition and the data type of the raw input data do not match, you will not get the expected results.
Valid in version: 2020.2.4 and later: The set of allowable characters for datasets dataset is a system property that the Administrator can configure. Navigation in the Akana Administration Console: Configuration tab > com.soa.analytics.console > analytics.validation.text.denylist.
Data Collection Using a Broker
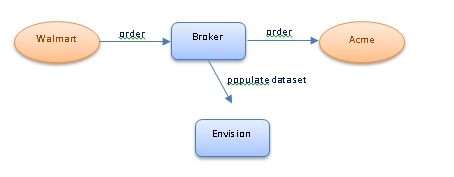
Envision on its own does not collect data. It only aggregates data based on the dataset definition. It does, however, provide an API that other systems and products can use to report the data they have collected that belong to a dataset. Envision also provides an API for defining the dataset itself so a system or product can create a dataset in Envision and then start reporting data that belongs to that dataset.
Other Akana products, when integrated with Envision, will install their own datasets and will collect data and feed it to Envision. The Akana API Gateway product will allow users to define metrics collection policies that are configured to extract data from business transactions that are processed by the API Broker. The policy defines instructions to the broker on how to extract information from a transaction and map it to a metric or dimension of a dataset in Envision.
Data Collection Using Individual Transactions or Raw Data
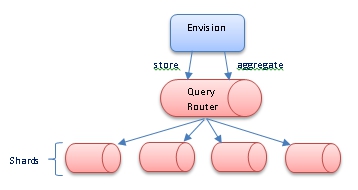
The Envision API will accept data from individual transactions (raw data) or pre-aggregated data. The API will persist the data in a MongoDB document data store. From here Envision will instruct the data store to aggregate the stored data on intervals that match those defined in the dataset. For example, if the dataset is defined to provide daily and weekly metrics then Envision will instruct the data store to aggregate the metrics on a daily and weekly basis.
The calculations performed by the data store to aggregate the metrics are dictated by Envision. Envision will consult the dataset definition and instruct the data store to perform the correct aggregation calculations. If the data store is clustered, or sharded, these calculations can span multiple instances providing the scalability that may be required for large volumes of data.