Using the Microsoft Azure Service Bus Relay Policy
Learn how to use the Microsoft Azure Service Bus Relay Policy to host your on-premise APIs in the Microsoft Azure cloud.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Microsoft Azure Service Bus Relay Policy is an Intermediary for Microsoft operational policy that is installed to the Policy Manager Management Console as part of the Intermediary for Microsoft product installation.
With this policy, you can host your on-premise APIs in the Microsoft Azure cloud. The policy offers Shared Secret or Access Control authentication modes.
To install this policy, see Chapter 3: Installing Akana Intermediary for Microsoft Policy Manager Policy section of the Akana Intermediary for Microsoft® Install Guide for installation instructions.
Configuration
Let's take a quick walkthrough of the Microsoft Azure Service Bus Relay Policy configuration process to get you started:
- Step 1: Add Policy
- Step 2: Modify Policy
- Step 3: Configure Policy
- Step 4: Attach Policy
- Step 5: Test Policy
Step 1: Add Policy
You can create a Microsoft Azure Service Bus Relay Policy instance using Add Policy in the Policies > Operational Policies section.
Step 2: Modify Policy
When you Modify the Microsoft Azure Service Bus Relay on the Policy Details page the initial policy will look like this:
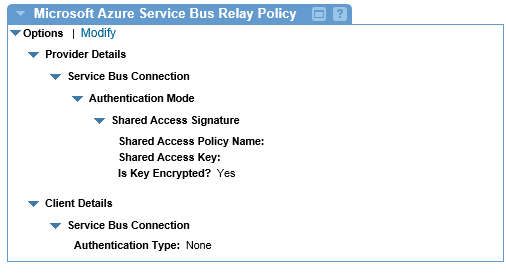
Step 3: Configure Policy
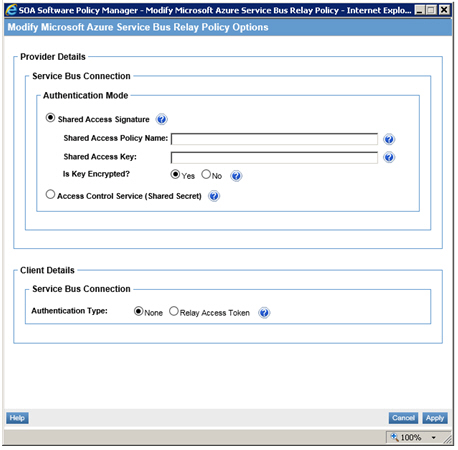
Configure the Microsoft Azure Service Bus Relay Policy as follows:
- Access Control Service (Shared Secret)—If you require that shared access keys remain private, encrypt the key using Akana's CryptoTool utility, enter that encrypted key for the shared access key, and declare the key encrypted here. See further Akana documentation on how to use the CryptoTool utility.
- Shared Access Key—Enter the shared access key, either primary or secondary, associated with the shared access policy entered above.
- Shared Access Policy Name—Each Microsoft Azure Service Bus namespace has a set of shared access policies used for authorization. Each policy grants certain access rights to Service Bus objects. Enter the name of the shared access policy that should be used for this connection.
- Service Bus Connection—Shared Access Signature is an authentication method that uses Microsoft Azure Service Bus's built in security model for authenticating providers. Shared Access Signature requires a Service Bus policy and associated key that providers will use to authenticate with Service Bus. Please see the Microsoft Azure Service Bus documentation for details.
- Access Control Service (Shared Secret)—Access Control Service (Shared Secret) is an authentication method that uses Microsoft Azure's Access Control Service to authenticate providers. Providers can authenticate with ACS using a pre-configured service identity and shared secret, which then federates with Microsoft Azure Service Bus. Please see Microsoft Azure Service Bus documentation for more information on this authentication mode.
- Client Details > Service Bus Connections—Enter the authentication mode that should be required of all clients connecting to Microsoft Azure Service Bus. If None is selected, any client can connect to Microsoft Azure Service Bus without needing to authenticate. If Relay Access Token is selected, all clients must first retrieve a valid relay access token, that Microsoft Azure Service Bus will first authenticate and authorize before allowing the client's transaction to proceed. Note that regardless of authentication mode, additional security can and should be used within the Policy Manager virtual service to ensure conformance to the required security policy.
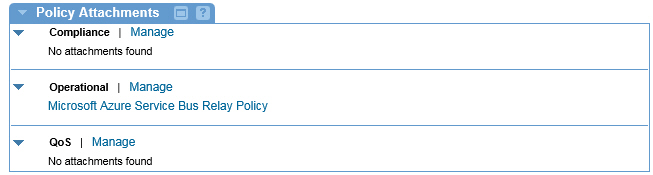
Step 4: Attach Policy
After you have saved your policy you can attach it to an Intermediary for Microsoft virtual Service in Policy Manager or you can attach the policy at the Organization level and the policy will be active for all services defined within the organization.
Step 5: Test Policy
After you attached the Microsoft Azure Service Bus Relay Policy to a virtual service, send a request to your service and view the results in your client. You can also go to the Services > Monitoring section to view the results for Logs (View Usage Record Details), Real Time Charts, and Historical Charts.
If you receive errors, review the log information for details. In most cases, errors are typically associated with specifying the wrong credentials for the Microsoft Azure Service Bus Provider. You may see errors when the service is first deployed to Intermediary for Microsoft and Intermediary for Microsoft connects to Microsoft Azure Service Bus using incorrect credentials. Update the credentials in the policy and retry.